Black Body Radiation Definition
The radiation maximum is centered in the band of radiation or visible light with a peak at 500 nm outside the Earths atmosphere. Therefore it does not focus on a single frequency.

Radical Black Body Radiation Courtney S Chemistry
Infrared or red radiation from a common household radiator or electric heater is an example of thermal radiation as is the heat emitted by an operating incandescent.
. Since these are simple harmonic oscillators the mean kinetic energy is equal to the mean potential energy so the total energy is kT. Non-ionizing radiation is any kind of radiation in the electromagnetic spectrum that does not have enough energy to remove an electron from an atom and turn it into an ionThis contrasts with ionizing radiation like x-rays gamma rays and alpha particles which come from the other end of the spectrum and are unstable and reactive. The skin protects us from microbes and the elements helps regulate body temperature and permits the.
Radiation therapy most often uses X-rays but protons or other types of energy also can be used. The skin is the largest organ of the body with a total area of about 20 square feet. Radiation heat transfer rate q Wm 2 from a body eg.
Radiation is absorbed and quickly reemitted by the walls which creates oscillations in the frequency of the radiation. The term radiation therapy most. In this article we will be learning about blackbody radiation and some important laws related to it.
Movies That Realistically Present Physics. Solar radiation definition. The mean thermal kinetic energy of an oscillating atom is 05 kT.
Black hole cosmic body of extremely intense gravity from which nothing not even light can escape. It has a specific continuous spectrum of wavelengths inversely related to intensity that depend only on the bodys temperature which is assumed for the sake of. Hawking radiation is an explanation of how radiation can be emitted from a black hole despite its attractive power due to quantum effects.
Or radiation. Q εσT 4. Where σ is a fundamental physical constant called the StefanBoltzmann constant which is equal to 5669710-8 Wm 2 K 4.
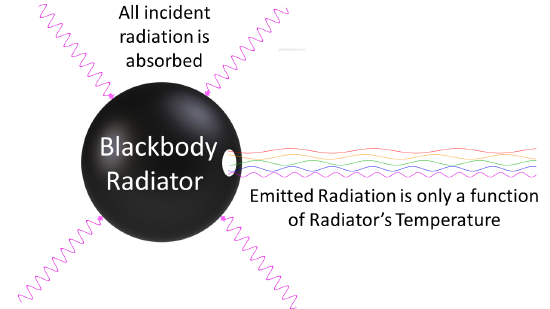
As is typical of the spectrum of a black body with which the solar source is modeled. A black body is an idealization in physics that pictures a body that absorbs all electromagnetic radiation incident on it irrespective of its frequency or angle. A black body to its surroundings is proportional to the fourth power of the absolute temperature and can be expressed by the following equation.
Black-body radiation is the thermal electromagnetic radiation within or surrounding a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment emitted by a black body an idealized opaque non-reflective body. A black hole can be formed by the death of a massive star. Hawking worked out the exact theoretical model for how a black hole could emit black body radiation.
Alpha radiation reduces the ratio of protons to neutrons in the parent nucleus bringing it to a more stable configuration. The first observations and investigation into alpha decay were made by Ernest Rutherford who used alpha particles in his gold foil scattering experiment. Non-Ionizing Radiation Definition.
The body uses L methionine to make creatine contains sulfur and is responsible for SAMe playing an important role in the proper function of the immune system neurotransmitters and cell membranes. Radiation therapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses beams of intense energy to kill cancer cells. An alpha particle is identical to the nucleus of a helium atom.
L methionine benefits include potentially helping reduce the risk of colorectal cancer lower tremors in those with Parkinsons build bone. Thermal radiation refers not only to the radiation itself but also the process by which the surface of an object radiates its thermal energy in the form of black body radiation. Black poop can be a side effect of iron pills you take for anemia-- a condition that happens when you dont have enough red blood cells to carry oxygen around your body.
Plancks radiation law a mathematical relationship formulated in 1900 by German physicist Max Planck to explain the spectral-energy distribution of radiation emitted by a blackbody a hypothetical body that completely absorbs all radiant energy falling upon it reaches some equilibrium temperature and then reemits that energy as quickly as it absorbs it. When such a star has exhausted the internal thermonuclear fuels in its core at the end of its life the core becomes unstable and gravitationally collapses inward upon itself and the stars outer layers are blown.

Colour Temperature Of Black Body Radiation Electrical4u

Black Body Radiation Powerpoint Slides

1 1 Blackbody Radiation Cannot Be Explained Classically Chemistry Libretexts

No comments for "Black Body Radiation Definition"
Post a Comment